Hybrid
Hybrid Solar System
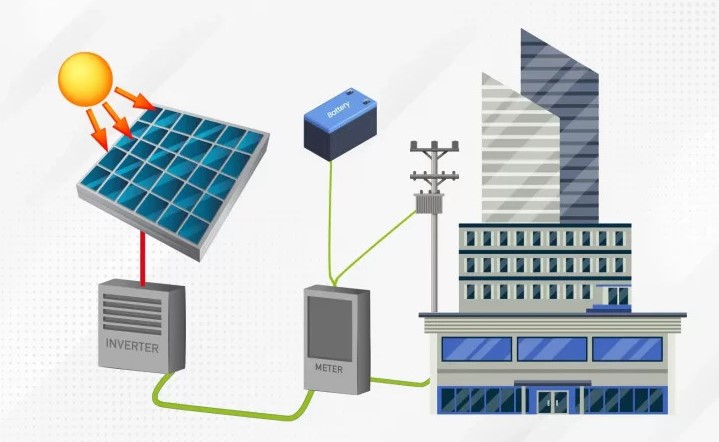
What is a Hybrid Solar System?
The functionality of this system starts from a Hybrid Solar Panel that helps to capture the sunlight and then convert it into DC (Direct Current) electricity. The DC electricity from the Hybrid Solar Panel is converted into AC (Alternating Current) with the help of an Inverter. Then the excess solar energy produced during the day is stored in a Battery Storage for use at night or on cloudy days for a continuous electricity supply. These systems combine the best features of grid-tied and off-grid solar systems, ensuring continuous solar power operation. When solar and battery energy are insufficient, then Grid Connection draws power from the grid and also exports excess energy to the grid. This way Hybrid Solar Systems can be used even during a blackout!
How Does a Hybrid Solar System Work?
- Solar Panels (PV Array) – They are installed on a rooftop or ground-mounted structure to get the maximum sunlight to convert solar energy into DC electricity.
- Inverters – They convert the DC electricity produced by Solar Panels into AC electricity which is then used by household appliances. There are some types of Inverters which contain string inverters, microinverters, and hybrid inverters all of which handle both solar and battery inputs.
- Batteries – These batteries store the extra solar energy generated so it can be used after sunset when there is low sunlight or on cloudy days. It contains a Battery Management System that helps monitor the charging and discharging of the battery to optimize its use and lifespan.
- Grid Connection – When the battery and solar energy are insufficient the grid connection helps to back up the power source and it allows the excess solar energy to be fed back to the grid. There are some areas where they can earn credits for exporting the excess energy to the grid.
- Energy Flow – To enhance the efficiency of the energy flow, Energy management helps to monitor and control its flow in the system. It also has smart technology which helps to store the power when it is most in demand.
- Storage Mechanism – It involves the use of batteries to save access to solar energy generated through solar panels. When the solar generation becomes low the batteries help to generate electricity so that there is no power outage.
Types of Hybrid Solar Panels
These types of Hybrid Solar Panels consist of Monocrystalline Solar Panel, Polycrystalline Solar Panel, Building Integrated Photovoltaic Solar Panel (BIPV), and Thin Film Solar Panel. Below is a brief description of each type with their pros and cons.
Monocrystalline Hybrid Solar Panel
Monocrystalline solar panels have solar cells made from a single crystal of silicon. The Crystalline purity of Monocrystalline is higher than that of Polycrystalline solar. The efficiency of monocrystalline solar panels varies from 16 to 24%. These Solar Panels have longer energy production periods.
Pros –
Monocrystalline has a longer lifespan, around 25 years or more warranty period.
If the space is limited in your premises then these solar panels are a perfect choice as these panels generate more electricity per square meter compared to any other solar panels. Therefore this type of solar panel has a higher efficiency rate
The generation of electricity is done early in the morning and till late in the evening in this type of solar panel as they have better performance in low light conditions.
Cons –
Monocrystalline and its production are expensive compared to any other solar panels.
During the production process of Monocrystalline, there is a waste of silicon as it is cut into silicon wafers from silicon cylindrical rods. This is one of the reasons for Monocrystalline to be expensive.
As Monocrystalline is made up of a single crystal structure it should be handled and installed with the utmost care as it is very fragile.
Polycrystalline Hybrid Solar Panel
This Solar Panel is made up of several fragments of silicon melted together. The efficiency rate of Polycrystalline is between 14 to 20 %. The Crystalline purity is less in Polycrystalline. The production period is less compared to monocrystalline panels.
Pros –
Production of Polycrystalline is less expensive than compared to monocrystalline which makes it lower in cost.
Wastage of the silicone is less as it is melted and then poured into square molds which results in less wastage.
It is a more environmentally friendly choice as the carbon footprints are less.
Cons-
It requires more space to generate the same amount of energy as compared to monocrystalline panels. So they are less space-efficient and the installation could be difficult.
It has a lower efficiency rate.
The purity scale of silicon in these panels is low and the end product may look less uniform in comparison to monocrystalline panels.
Building Integrated Photovoltaic Solar Panel (BIPV)
It is a solar power-generating product or system that is integrated into the parts of a building such as roofs and windows. This solar panel uses one of these two technologies: crystalline solar cells and Thin Film Solar cells. The average efficiency of this panel is around 5 to 10 %.
Pros –
These types of panels are designed to appear visually appealing. It integrates into the architecture of the building smoothly.
With the help of this system, electricity is generated on-site which helps save energy costs and also lowers utility bills.
When you opt for these panels, the Government offers incentives or subsidies for integrating this system into their buildings which attracts more investments in such technologies.
Cons –
Installation of this type of panel requires proper planning to not mess with the buildings’ design and construction.
As the installation process is complex, the repair and maintenance of these panels are also expensive.
The efficiency is directly dependent on the design, location, and orientation of the building.
Thin Film Solar Panel
Like other solar panels, thin-film panels convert light energy into electrical energy via the photovoltaic effect. Unlike traditional systems, thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible second-generation cells. Each cell consists of three main parts: photovoltaic material, a conductive sheet, and a protective layer. There are various types of Thin Film Solar Panel namely amorphous silicon (a-Si) panels, Cadmium telluride (CdTe) panels, Copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) panels, and Organic photovoltaic (OPV) panels.
Pros –
These types of panels are generally lightweight and easy to install.
Thin Film Panels work well in low-light conditions making them more reliable.
The manufacturing cost is low as compared to other silicon panels.
These types of Hybrid Solar Panels consist of Monocrystalline Solar Panel, Polycrystalline Solar Panel, Building Integrated Photovoltaic Solar Panel (BIPV), and Thin Film Solar Panel. Below is a brief description of each type with their pros and cons.
Monocrystalline Hybrid Solar Panel
Monocrystalline solar panels have solar cells made from a single crystal of silicon. The Crystalline purity of Monocrystalline is higher than that of Polycrystalline solar. The efficiency of monocrystalline solar panels varies from 16 to 24%. These Solar Panels have longer energy production periods.
Pros –
- Monocrystalline has a longer lifespan, around 25 years or more warranty period.
- If the space is limited in your premises then these solar panels are a perfect choice as these panels generate more electricity per square meter compared to any other solar panels. Therefore this type of solar panel has a higher efficiency rate
- The generation of electricity is done early in the morning and till late in the evening in this type of solar panel as they have better performance in low light conditions.
Cons –
- Monocrystalline and its production are expensive compared to any other solar panels.
- During the production process of Monocrystalline, there is a waste of silicon as it is cut into silicon wafers from silicon cylindrical rods. This is one of the reasons for Monocrystalline to be expensive.
- As Monocrystalline is made up of a single crystal structure it should be handled and installed with the utmost care as it is very fragile.
- Polycrystalline Hybrid Solar Panel
This Solar Panel is made up of several fragments of silicon melted together. The efficiency rate of Polycrystalline is between 14 to 20 %. The Crystalline purity is less in Polycrystalline. The production period is less compared to monocrystalline panels.
Pros –
- Production of Polycrystalline is less expensive than compared to monocrystalline which makes it lower in cost.
- Wastage of the silicone is less as it is melted and then poured into square molds which results in less wastage.
- It is a more environmentally friendly choice as the carbon footprints are less.
Cons-
- It requires more space to generate the same amount of energy as compared to monocrystalline panels. So they are less space-efficient and the installation could be difficult.
- It has a lower efficiency rate.
- The purity scale of silicon in these panels is low and the end product may look less uniform in comparison to monocrystalline panels.
Building Integrated Photovoltaic Solar Panel (BIPV)
It is a solar power-generating product or system that is integrated into the parts of a building such as roofs and windows. This solar panel uses one of these two technologies: crystalline solar cells and Thin Film Solar cells. The average efficiency of this panel is around 5 to 10 %.
Pros –
- These types of panels are designed to appear visually appealing. It integrates into the architecture of the building smoothly.
- With the help of this system, electricity is generated on-site which helps save energy costs and also lowers utility bills.
- When you opt for these panels, the Government offers incentives or subsidies for integrating this system into their buildings which attracts more investments in such technologies.
Cons –
- Installation of this type of panel requires proper planning to not mess with the buildings’ design and construction.
- As the installation process is complex, the repair and maintenance of these panels are also expensive.
- The efficiency is directly dependent on the design, location, and orientation of the building.
Thin Film Solar Panel
Like other solar panels, thin-film panels convert light energy into electrical energy via the photovoltaic effect. Unlike traditional systems, thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible second-generation cells. Each cell consists of three main parts: photovoltaic material, a conductive sheet, and a protective layer. There are various types of Thin Film Solar Panel namely amorphous silicon (a-Si) panels, Cadmium telluride (CdTe) panels, Copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) panels, and Organic photovoltaic (OPV) panels.
Pros –
- These types of panels are generally lightweight and easy to install.
- Thin Film Panels work well in low-light conditions making them more reliable.
- The manufacturing cost is low as compared to other silicon panels.
Cons –
- This type of solar panel has a shorter operational lifespan.
- Thin Film Solar panels have a lower Efficiency rate compared to other crystalline silicon panels.
- The thin film panels use cadmium and are difficult to dispose of so it concerns the Environment.
This type of solar panel has a shorter operational lifespan.
Thin Film Solar panels have a lower Efficiency rate compared to other crystalline silicon panels.
The thin film panels use cadmium and are difficult to dispose of so it concerns the Environment.
